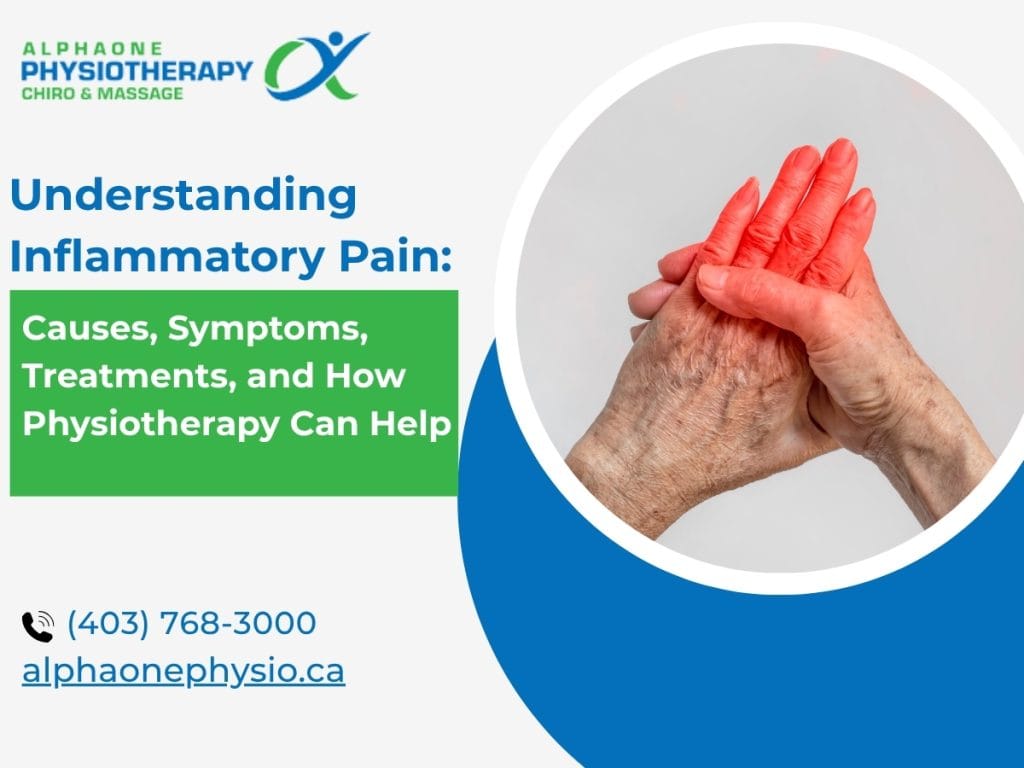
nflammatory pain happens when something inside your body becomes swollen or irritated. This is how your body tries to heal itself. When you get hurt or fall sick, your body sends more blood and special healing cells to that part. This process is called inflammation.
In the beginning, inflammation is helpful. It helps your body fix the damage. But if it stays for too long or becomes too strong, it can start to cause pain instead of helping you feel better.
You may not always notice inflammation right away. Sometimes it feels like a deep, dull ache. Other times, it can feel like a burning or throbbing pain. It can also feel sharp. You do not always need a visible injury to have this kind of pain. It can also happen from stress, bad sitting or standing habits, or certain health problems.
Inflammation is often the hidden reason behind joint pain, tight muscles, back pain, and even feeling tired all the time. Many people have this pain every day and do not realise that inflammation could be the cause.
What Causes Inflammatory Pain?
There are many reasons why a person may have inflammatory pain. Sometimes, it happens because of an injury. Other times, it comes from things we do every day. It can also be caused by health problems that last for a long time.
Injuries from daily life or sports
If you twist your ankle, pull a shoulder muscle or fall down, it can cause swelling for a short time. This happens because the tissues inside your body get hurt. Your body starts to heal by making the area swell. But if you do not take care of the injury the right way, the swelling can stay for a long time and the pain might last for weeks or even months.
Autoimmune diseases
Some health problems like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus or multiple sclerosis happen when the body starts to attack its own healthy parts by mistake. This leads to swelling inside the joints, muscles or organs. The swelling stays for a long time and causes constant pain and stiffness.
Repetitive strain or overuse
When you repeat the same movement many times, like typing, lifting things, bending or using your phone for hours, it can slowly hurt your muscles and joints. If this keeps happening every day, it can lead to long-lasting swelling in places like your wrists, elbows, shoulders and lower back.
Poor posture or long periods of sitting
If you sit with a bent back, your head pushed forward or your shoulders dropped, it can put extra pressure on your spine and joints. Over time, this can cause swelling and pain in your neck, upper back or hips. This is common in people who sit at a desk or drive for many hours each day.
Chronic stress or lack of sleep
Stress changes how your body reacts. It increases certain hormones like cortisol, which can lead to long term inflammation. Lack of sleep also makes the body weaker and less able to fight pain or heal itself.
A report in NIH found that over 50% of all deaths worldwide are linked to diseases that involve inflammation. These include diabetes, heart disease and joint disorders.
What Are the Symptoms of Inflammatory Pain?
You can often tell if your pain is from inflammation by the way it feels and how your body reacts. Below are some common signs to look for:
- Redness and warm skin: If one part of your body feels hot or looks red, even when you do not have a fever, it might be due to swelling inside. This happens because more blood goes to that area. You may feel heat when you touch the spot.
- Swelling near joints or muscles: You may notice puffiness or a soft bump under your skin. This usually happens around your joints or muscles. The swollen area might hurt when you touch it. It can also make it hard to move that joint properly.
- Pain that gets worse when resting: The pain often feels stronger when you are still for a long time with inflammation. For example, your body may feel stiff when you wake up in the morning or after sitting for too long. Unlike regular muscle pain, this pain does not go away with rest.
- Feeling tired or low on energy: Inflammation does not just affect one area. It can make your whole body feel weak. You might feel very tired, even if you did not do much. It can also make it hard to sleep or focus on things.
- Stiff joints and hard movement: Many people with inflammation feel very stiff, especially after waking up. It may feel like your joints are stuck or not moving smoothly like before.
Health Conditions That Cause Inflammatory Pain
Inflammatory pain can show up in many forms depending on the condition. Here are some common ones:
- Rheumatoid arthritis: This is an autoimmune condition where the body attacks its own joints. It leads to swelling, stiffness and pain, mostly in the hands, feet and knees.
- Tendinitis: This is when tendons (the tissues that connect muscles to bones) get inflamed. It often affects the shoulder, elbow or ankle, especially in people who play sports or do physical work.
- Bursitis: Bursae are tiny fluid filled sacs near your joints. When these get irritated, they cause pain, swelling and limited movement in areas like the hip, knee or shoulder.
- Plantar fasciitis: This condition causes pain in the heel or bottom of the foot due to inflammation in the tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes.
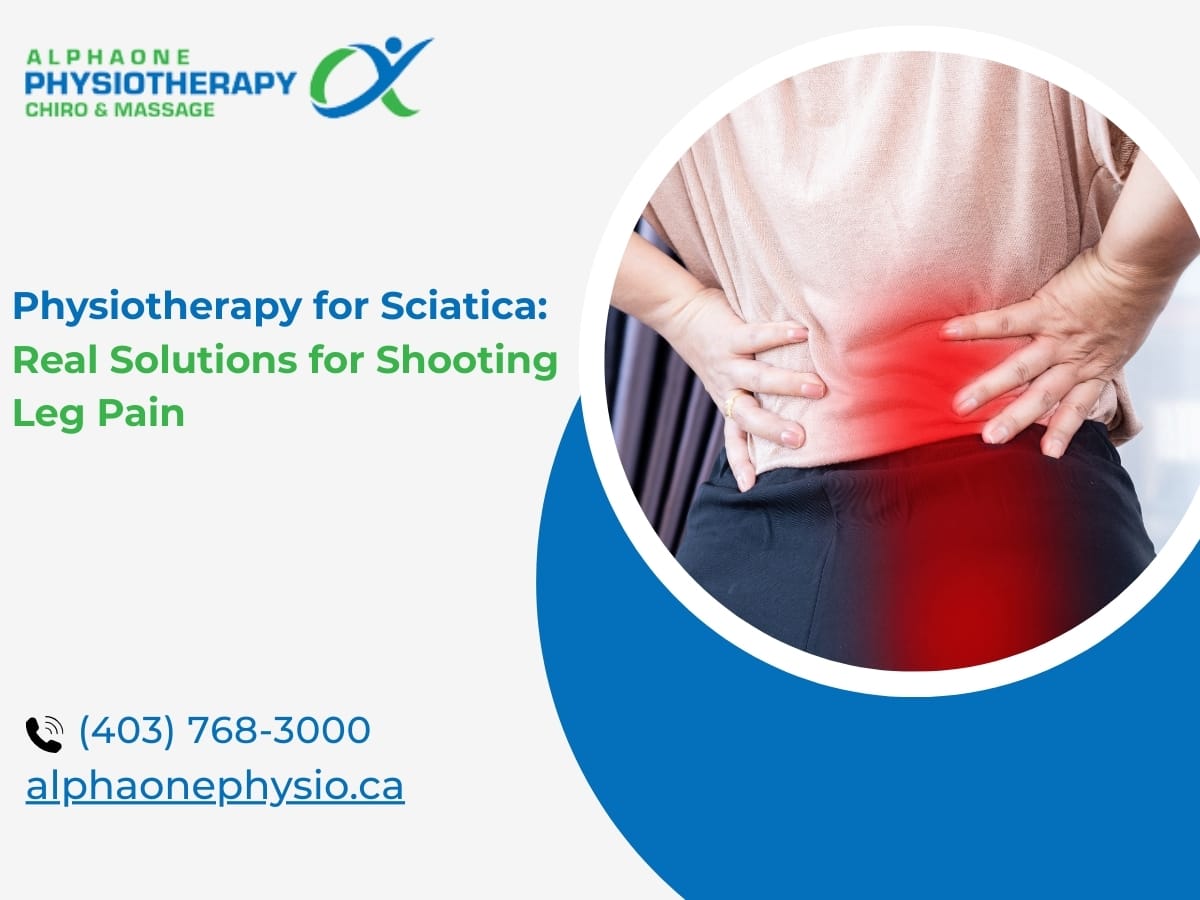
- Sciatica and back pain: Inflammation in the lower back or spine can press against nerves and lead to sharp pain down the leg or back. It can come from sitting too long or heavy lifting.
“The pain of inflammation is not the enemy. It’s your body’s way of asking for help.” — Dr. Janet Travell
What Can You Do to Manage Inflammatory Pain?
You don’t always need strong medicine to manage inflammatory pain. Many small changes can make a big difference.
Rest but not too much
Giving your body time to recover is important, especially after an injury. But too much rest can stiffen your joints. Gentle movement keeps your blood flowing and helps healing.
Apply ice or heat as needed
Ice packs help reduce swelling after a fresh injury. Heat works well for stiffness and sore muscles. Use each for 15 20 minutes at a time, based on how your body feels.
Eat anti inflammatory foods
Foods like turmeric, ginger, green leafy vegetables and berries can lower inflammation naturally. Avoid sugary snacks and processed foods, as they can make inflammation worse.
Stretch and move gently
Simple exercises like walking, yoga or light stretching can keep your joints flexible and reduce pain over time. Do what feels comfortable and increase slowly.
Practice stress relief and good sleep habits
Relaxation, deep breathing and getting 7–8 hours of sleep every night gives your body the strength to heal. Meditation or spending time in nature also helps reduce inflammation.
How Physiotherapy Can Help With Inflammatory Pain
Physiotherapy is one of the best long term ways to treat and manage inflammatory pain. It doesn’t just cover up the pain, it helps your body recover and grow stronger.
- Personalised exercises made just for you: Physiotherapists create safe, gentle routines that target the areas causing pain. These movements help stretch tight muscles, improve joint movement and build strength over time.
- Manual therapy and pain relief techniques: Hands on treatments like massage, dry needling, cupping or joint mobilisation help reduce swelling, ease tension and relax the muscles. They improve blood flow and support healing.
- Posture correction and movement education: You will learn how to sit, stand, sleep and move in ways that protect your joints and reduce pain in daily life.
- Advanced tools for recovery: Physiotherapy can include treatments like ultrasound, electrical therapy (TENS) or shockwave therapy. These tools target inflammation directly and speed up healing.
- Ongoing support and prevention: Physiotherapists don’t just treat your pain once. They help you stay pain free in the future by building habits and movements that prevent flare ups.
A recent study published in The Medical Rehabilitation Centre showed that patients with chronic pain who followed a 12 week physiotherapy plan had a 65% improvement in mobility and function.
Final Thoughts
Living with inflammatory pain can be hard. It affects how you move, work, and enjoy life. But the good news is, it doesn’t have to stay that way. When you understand the cause of the pain and treat it early, you can take back control.
By resting the right way, eating healthy, staying active, and reducing stress, you give your body a strong chance to heal. And with professional help like physiotherapy, you can speed up recovery and get long-lasting results.
AlphaOne Physiotherapy works with people facing inflammatory pain every day. Our team takes time to understand your pain and guide you through safe, effective steps to get better. Whether your pain is new or has been there for years, we’re here to help you move with comfort and confidence again.
Frequently Asked Questions
The main reason for inflammatory pain is swelling inside the body. This happens when the body reacts to an injury, infection or long term stress. The swelling can press on nerves and tissues, causing pain, stiffness and discomfort in different areas.
You can tell if your pain is from inflammation by noticing signs like swelling, redness, warmth or stiffness. The pain often feels worse after rest. It usually lasts longer than regular muscle soreness and does not go away on its own easily.
Yes, physiotherapy can help reduce inflammatory pain safely. It includes gentle exercises, manual therapy and posture correction. These treatments lower swelling, improve movement and prevent pain from returning. A trained physiotherapist makes a personalised plan based on your body’s needs and condition.
Sitting for long hours, eating processed or sugary foods, poor sleep and high stress can all increase inflammation. These habits put pressure on your body’s joints and muscles. Over time, they can lead to chronic pain and long term health problems if ignored.
The time to recover depends on how severe the inflammation is and how early treatment starts. Some people feel better in a few weeks, while others may need longer care. Following a proper routine and physiotherapy plan helps speed up the healing process.